Are you looking for a food allergy specialist in Barcelona?
Food allergies affect approximately 2-4% of the global population, i.e. around 150-300 million people.
Diagnosing food allergies is essential for several key reasons, the most important being the prevention of severe reactions. An accurate and early diagnosis will also optimise quality of life, facilitate proper dietary management and give the patients and their families a sense of security and control over their health.
Our specialist will diagnose and design a personalised plan to treat and manage your food allergy in the most manageable way possible.
Is a food allergy the same as an intolerance?
Food allergies occur in people who have a specific genetic predisposition that can lead the immune system to generate an altered response. These responses tend to trigger the effects or signs that we attribute to allergic reactions. The key part is that they are an immune response.
Intolerances, although similar, arise from alterations in digestion or food metabolism, not from the immune system. Typically, these disorders are the result of enzyme deficiencies or susceptibility to certain food components.
A clear example of the difference between allergy and intolerance is found in milk. Some people have a milk allergy because their immune system produces IgE antibodies in response to certain proteins present in milk. In contrast, people with milk intolerance do not produce lactase, the enzyme in the gut that breaks down lactose, the natural sugar in milk. As a result, when they consume milk, lactose is not properly digested in the intestine and reaches the colon, where it is fermented by the bacterial flora, triggering digestive manifestations such as gas.
What are the most common allergy-causing foods?
- Milk (cow's milk): one of the most common allergies, especially in children under 3 years of age.
- Eggs: another common allergen in children, although with age, this allergy usually disappears.
- Fish: can include several species.
- Shellfish: the most common are crustaceans and molluscs.
- Peanuts: one of the most common among adults.
- Nuts: the most common include walnuts, almonds, hazelnuts and cashews. Peanut and tree nut allergy remits in one in five patients.
- Wheat: also one of the best known, affecting more children than adults, as at a certain age, many children outgrow this allergy.
- Soya: like wheat, it is more common in children and is usually outgrown with age.
The prevalence and types of allergens often vary according to geography and dietary habits, with some regions or cultures having other foods that are common allergens, such as sesame, certain fruits or seeds.
What does a food allergy look like?
Allergic reactions appear within 2 hours after ingestion of the food, but usually within the first 30-60 minutes.
Reactions may affect one or more organs such as the skin, digestive tract, respiratory and cardiovascular system. The most common reactions are skin reactions in the form of hives, oral and pharyngeal mucosa reactions in the form of local itching, and digestive reactions such as vomiting, diarrhoea or abdominal pain.
Respiratory problems such as rhinitis and bronchospasm are also possible. The latter occurs mainly in cases of anaphylaxis in asthmatics; it can be extremely severe and is generally the leading cause of death in food reactions, which is why it is important to act quickly in response to such an immune response.
The severity of an allergic reaction depends on a number of factors, including the characteristics of the food allergen, the patient's immune response, the patient's ability to compensate physiologically and risk factors such as additional diseases the patient may have (cardiovascular problems, asthma or acute infections).
Are food allergies permanent?
Allergies to foods such as milk, egg, soya and certain cereals that occur in the first years of life usually disappear naturally. About 80 % of milk-allergic children and more than 50 % of egg-allergic children outgrow the allergy by the age of five. But nut and peanut allergy usually persists in about four out of five patients. Allergies to other foods tend to be long-lasting in most cases and it is difficult to say how often they subside.
How is the diagnosis of a food allergy carried out at Turó Park Clinics?
The diagnosis of food allergies is a fairly similar process in all cases.
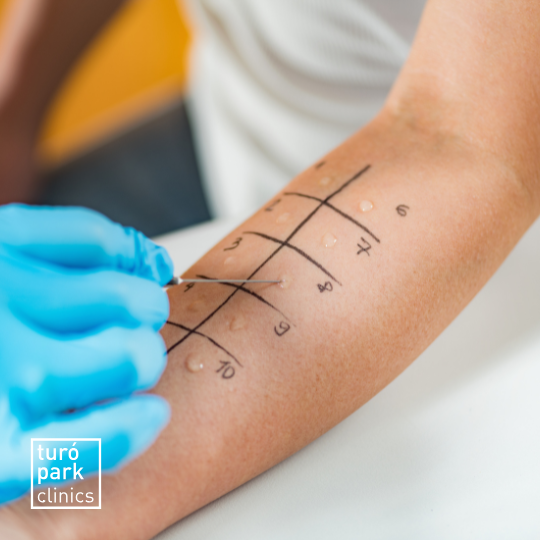
On the first visit, our specialist will study your medical history, evaluate your symptoms and possible triggers. It is very likely that diagnostic tests will be carried out to determine the root cause of the allergy, including prick tests and blood tests.
In addition, other tests such as stool tests or controlled exposure tests with the suspected food are common.
Who is recommended to get tested?
The recommendation for food allergy testing is based on factors such as symptoms, age and medical history. It is indicated for:
- People with a history of allergic reactions after consuming certain foods
- Children with persistent atopic dermatitis
- People with a family history of food allergy
- People who already have allergies to other foods or allergic conditions
- Patients with chronic digestive symptoms with no apparent cause
- Infants with adverse reactions to the introduction of new foods
Your health is our priority!
Our allergology department welcomes you to the diagnosis and treatment of food allergies.

Our specialist
