Have you noticed a change in your moles and are looking for a dermatologist in Barcelona?
Skin cancers are by far the most common cancers in humans. Melanomas, which account for 10% of skin cancers, are responsible for the majority of deaths from skin cancer because of their high metastatic potential. They affect all age groups, with a peak in rates in people between 30 and 50.
Therefore, early detection is a priority as it offers a better chance of cure. It is recommended that whole skin be checked annually for suspicious moles that could be cancerous, especially for people with fair skin and a history of sun exposure or a family history of skin cancers.
Make an appointment now with one of our dermatologists to schedule your full dermatological examination.
Fast track your treatment
To book an appointment or speak with one of our friendly team, please get in touch using the options below.
Who should undergo skin screening?
Each individual has a different skin sensitivity linked to his or her genetic make-up, which defines the skin's natural ability to protect itself from the sun. More specifically, those most at risk of developing skin cancer are those with a pale complexion, blond or red hair, a high sensitivity to sunburn and a low ability to tan.
It is therefore particularly important to see a dermatologist for skin screening if you have:
- Have fair skin or hair
- Had many sunburns in the past
- Have many moles
- A family history of melanoma
- Had significant sun exposure (occupational or recreational).
However, an annual dermatological check-up is also recommended for the general population, as well as a regular self-assessment of the skin.
How to detect a melanoma early?
Melanomas can be diagnosed and recognised by every individual who has been made aware of mole screening.
The "ABCDE rule" can help to recognise the warning signs of melanoma*:
*Caution: the presence of one or more of these criteria does not necessarily imply skin cancer, but should lead you to refer the patient to a dermatologist as soon as possible.
How is melanoma diagnosed?
Preliminary questioning
In the presence of a suspicious skin lesion, the doctor begins by questioning the patient to look for risk factors for melanoma (family history, prolonged exposure to the sun, phototype, etc).
Examination of suspicious moles or lesions
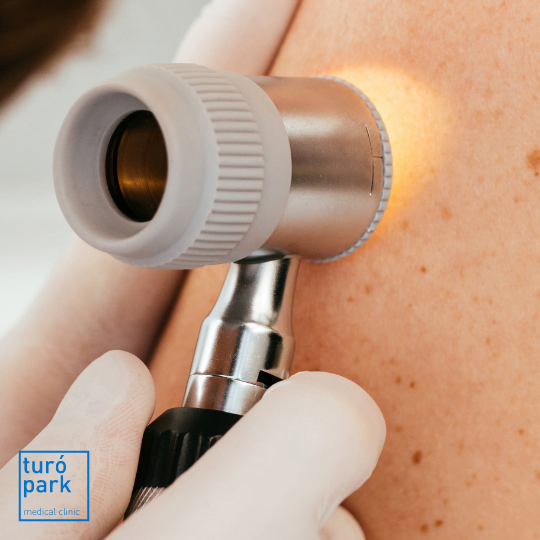
They then examine the lesion and the whole of the skin of the body, sometimes using a magnifying optical device, to look for possible lesions. In some cases, especially when patients have multiple irregular moles (atypical nevi), mole mapping may be considered. This involves photographing and locating all the nevi (moles) on the skin on a map of the body, but also taking images of some of them with an epiluminescence microscope or digital dermatoscope, a piece of technology that allows you to see data about the structure of the nevi that can indicate whether they are benign or malignant.
Analysis and diagnosis
The suspected lesion is removed in its entirety and then analysed to confirm the diagnosis or not. If the diagnosis is confirmed, other tests may be ordered depending on the type of melanoma and its stage of development: blood tests, abdominal ultrasound, thoraco-abdomino-pelvic scanner, brain MRI, etc.
How to limit the risk of skin cancer?
It is possible to prevent skin cancer with a few simple actions:
- Avoid the sun between 11am and 4pm.
- Expose yourself gradually avoiding sunburn.
- Protect children with a hat, T-shirt and sunglasses.
- Do not expose children under the age of one.
- Avoid tanning booths (solarium).
We take care of your skin.
Our dermatologists welcome you for personalized care of all your skin, hair and nail problems.

Our English-speaking dermatologists


