Thyroid nodules or nodular thyroid disease is a common thyroid condition. Anyone can have a thyroid nodule, but it becomes more common as people age, with women being more likely to develop nodules on the thyroid gland than men.
Since most nodules don’t cause noticeable symptoms, people don’t realize they have a thyroid gland problem. In other cases, the nodules can grow much larger, causing problems like a noticeable lump in the neck, difficulty breathing, etc. But the good news is that no matter how large a thyroid nodule is, it can be easily treated. And our skilled endocrinologists at Turó Park Clinics can help.
Our doctors have extensive experience in treating thyroid nodules. In addition, they curate personalized treatment plans for each patient to ensure the best outcomes. So, if a nodule on your thyroid gland is bothering you, book a consultation today at our thyroid nodule clinic in Barcelona.
Treatment information
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Name | Thyroid Nodules |
| Doctor | Carla Font |
| Diagnosis | Blood test or physical exam. |
Fast track your treatment
To book an appointment or speak with one of our friendly team, please get in touch using the options below

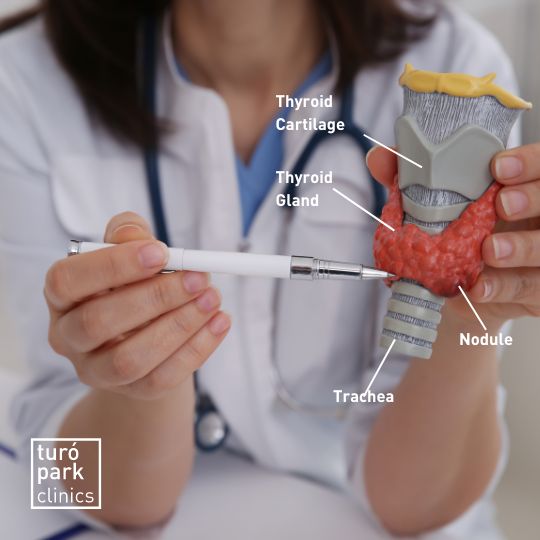
What Are Thyroid Nodules?
The thyroid gland is a small, butterfly-shaped endocrine gland located at the front of your neck, right below the Adam’s apple or just above the breastbone. It produces the hormones thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) that control several bodily functions. These include metabolism, mood, body temperature, heart rate, and digestion.
Sometimes, little lumps or bumps form on the thyroid gland. These are called thyroid nodules. Nodules in the thyroid gland can be:
- Solitary – a single nodule
- Multiple – two or more nodules
- Cystic – Fluid-filled nodules
- Solid
- Hot Nodule – produces thyroid hormones
- Cold Nodule – Doesn’t produce thyroid hormones
Nodules on the thyroid gland aren’t usually painful. Nonetheless, sometimes nodules can be a sign of or lead to other thyroid diseases.
Your health is our priority!
Our endocrinology department welcomes you for the diagnosis and treatment of all your endocrine disorders.
What Causes The Formation Of Nodules In The Thyroid Gland?
Thyroid nodules can form for various reasons. Sometimes, the exact cause isn’t clear. Here are a few factors that contribute to nodular thyroid disease.
| Thyroid Disorder | Symptoms | Causes | Diagnosis | Treatment | Risks | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hypothyroidism | Fatigue, weight gain, constipation, dry skin, hair loss | Lack of thyroid hormone production | Blood test | Thyroid hormone replacement medication | Hypothyroidism can be a chronic condition, but it can be managed with medication. | Most people with hypothyroidism can live a normal life with treatment. |
| Hyperthyroidism | Weight loss, anxiety, heat intolerance, irregular heartbeat | Too much thyroid hormone production | Blood test | Medication to reduce thyroid hormone production, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery | Hyperthyroidism can be a serious condition, but it is usually treatable. | Most people with hyperthyroidism can return to their normal activities after treatment. |
| Thyroiditis | Inflammation of the thyroid gland | Autoimmune disease, infection, radiation treatment | Blood test | Medication to reduce inflammation, pain relievers, or surgery | Thyroiditis is usually a temporary condition, but it can sometimes lead to hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism. | Most people with thyroiditis recover completely. |
| Goiter | Enlargement of the thyroid gland | Too much or too little thyroid hormone production, iodine deficiency | Physical exam, ultrasound | Medication to reduce thyroid hormone production, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery | Goiter is usually a benign condition, but it can sometimes be a sign of a more serious underlying disorder. | Most people with goiter can live a normal life with treatment. |
| Thyroid cancer | A tumor of the thyroid gland | Unknown | Physical exam, biopsy | Surgery, radiation therapy, or radioactive iodine therapy | Thyroid cancer is a serious but treatable condition. | Most people with thyroid cancer can be cured with treatment. |
→ Thyroid Tissue Overgrowth
One of the common thyroid gland nodules causes is tissue overgrowth, referred to as thyroid adenoma. The reason for thyroid adenoma is unclear. However, it is non-cancerous (benign). The tissues may grow larger than the surrounding tissues and form nodules, but they don’t spread beyond the thyroid gland. Hence, it isn’t considered serious unless it leads to further issues like hyperthyroidism.
→ Iodine Deficiency
The thyroid gland uses iodine to synthesize thyroid hormones. When your diet lacks iodine, the thyroid gland might try to compensate for the deficiency by growing and forming nodules. In addition, iodine deficiency can lead to goiter, an enlargement of the thyroid gland. A multinodular goiter contains several nodules on the thyroid within the goiter.
→ Inflammation Of The Thyroid
Disorders of the thyroid gland, like Hashimoto’s disease, cause thyroid inflammation. Long-term inflammation leads to the development of enlarged thyroid nodules. It is typically associated with hypothyroidism.
→ Thyroid Cysts
Degenerating thyroid adenomas lead to fluid-filled sacs within the thyroid gland, known as thyroid cysts. They are either entirely filled with fluid or both solid and fluid. Thyroid cysts are benign but might contain cancerous solid components. They can also cause some discomfort. Generally, cysts are biopsied if they grow larger than 2 centimeters.
→ Thyroid Cancer
The chances of nodules on the thyroid gland being cancerous are small. According to studies, around 90% of detected nodules in adults are benign nodules (non-cancerous). However, there still exists a 4.0% to 6.5% chance of nodules representing thyroid cancer.
Certain factors increase the susceptibility to thyroid cancer. These include a family history of thyroid or other endocrine cancers, a history of radiation exposure from medical therapy, etc.
Large nodules on the thyroid that are hard and cause pain or discomfort demands medical attention.
Apart from these five conditions, other factors that can contribute to thyroid nodules include:
- Genetic predisposition
- Exposure to radiation
- Aging
- Iron-deficiency anemia
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Alcohol consumption
- Metabolic syndrome
- Uterine fibroids
- Increased levels of insulin-like growth factor-1
How Are Nodules On The Thyroid Gland Diagnosed?
Sometimes you feel or see a lump in your neck. Or, you might have gone for a routine physical checkup, and your healthcare provider discovered it. A nodule may also be found during an imaging test performed for a different reason.
As mentioned earlier, benign thyroid nodules aren’t something that needs to be worried about. But the fact that there is a slight chance for the nodule to be cancerous demands some type of evaluation. At Turó Park Clinics, our endocrinologist may recommend any of the following tests to determine the presence of a nodule on your thyroid gland.
Thyroid Blood Test: To measure the level of thyroid hormones. Usually, nodules don’t affect the hormone levels much. But in some cases, an abnormal level can be linked to an underlying thyroid disorder.
Thyroid Ultrasound: Sound waves are used to create images of the thyroid gland and any nodules on it. This imaging test helps determine nodules' size, shape, and characteristics, such as whether you are solid-filled, fluid-filled, or both.
Fine-Needle Aspiration (FNA) Biopsy: If a nodule appears suspicious on ultrasound or has risk factors, the endocrinologist will recommend a fine-needle aspiration biopsy. During this procedure, a thin needle is used to extract a small sample of cells from the thyroid nodule. The sample is then sent for laboratory examination to determine if the nodule is benign, cancerous, or indeterminate.
Thyroid Scan: It is performed to evaluate the activity of the nodules. This involves swallowing a small amount of radioactive iodine and having images taken to see how the nodules function–how much iodine the nodules absorb and how much the normal thyroid tissue absorbs.
Depending on the results of these tests, your thyroid nodule doctor will decide the appropriate course of action.
How Are Thyroid Nodules Treated Or Managed?
The nodules treatment approach depends on several factors, such as its size, whether it's cancerous or benign, the symptoms it causes, etc. Common thyroid nodule treatment options include:
Observation:
If the thyroid nodule is small and non-cancerous, your healthcare provider might suggest monitoring it over time. You will visit your doctor regularly for check-ups and ultrasound exams to track any changes in the size or appearance of the nodule.

Radioiodine Therapy:
Thyroid nodules that produce excessive hormones (hyperfunctioning) or goiters with several nodules can be treated using radioiodine therapy. The thyroid gland will absorb the radioactive iodine causing the nodules to shrink in size. Nonetheless, pregnant or breastfeeding women aren’t given this treatment.
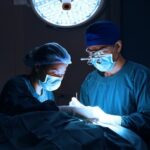
Surgery:
Surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland is the best option for cancerous nodules or nodules that obstruct breathing or swallowing.

Radiofrequency Ablation:
For thyroid nodules that are small and benign, radiofrequency ablation is used. Thyroid nodule ablation is performed in an office setting where a probe is used to access the benign nodule and destroy it using heat generated from high-frequency electrical current. The process is relatively simple, and patients, after treatment, can resume normal activities the next day.
Our multilingual endocrinology doctors


