Are you looking for an allergologist in Barcelona?
Are you experiencing skin rashes, itching, breathing difficulties, nasal congestion or gastrointestinal problems that are difficult to explain, these symptoms may be due to allergic reactions.
At Turó Park Clinics we have an allergologist who specialises in diagnosing, treating and developing specific immunotherapy plans to manage and prevent the symptoms of allergic diseases.
What is an allergy?
Allergic diseases, also known as hypersensitivity diseases, are caused by an exaggerated reaction of the immune system to various substances in the environment known as allergens. These allergens are typically non-hazardous substances for non-allergic people, but when they come into contact with the immune system of somebody allergic, they have the ability to induce the production of specific antibodies, called immunoglobulin E. These antibodies trigger the release of inflammatory substances responsible for the symptoms that constitute what we known as an allergic reactions. The severity of allergic reactions varies according to the type of allergen involved and the sensitivity of each patient.
Technically any substance can be an allergen. Some are found in suspension in the air and are breathed in (pollen, mites, animal epithelia), but they can also be found in food, medicines, etc.
To book an appointment or speak with one of our friendly team, please get in touch using the options below.
What is the difference between a food allergy and a food intolerance?
A food allergy and a food intolerance are two types of adverse reactions to certain foods but with different mechanisms, symptoms and consequences.
The mechanism of an allergy is controlled by the immune system while the mechanism of an intolerance is controlled by the digestive system. In an allergy, our immune system mistakenly identifies a food protein as a threat, thus producing antibodies to fight it. In an intolerance, our digestive system is unable to break down certain foods or components, usually due to a lack of digestive enzymes.
The response of the immune system, in the case of allergies, and the digestive system, in the case of intolerances, is manifested in the form of symptoms that we associate with these two conditions.
Allergies are generally considered to be more serious, as their reactions are rapid and can occur with a very small amount of the allergen. They tend to cause more severe reactions and can be life-threatening. In the case of intolerances, symptoms usually appear gradually and often require a larger amount of the food to trigger symptoms.
What are the most common allergies?
Allergic diseases are very common and are estimated to affect 20-25% of the global population, especially children and young people. They are more common in developed and industrialised countries than elsewhere.
Among the reasons for consultation, respiratory allergies are the most frequent, followed by atopic dermatitis and food allergies. Nevertheless, there are other types such as drug allergies, allergies to the venom of the himenoptera species , angioedema and hives, mastocytosis, etc.
Some of the most common allergic reactions we treat include:
- Asthma: is a chronic inflammatory disease of the airways that causes episodes of reversible airflow obstruction and is characterised by coughing, shortness of breath, wheezing or a feeling of tightness in the chest. It is a very prevalent disease, being one of the most frequent chronic diseases in the paediatric age group. It is determined by a genetic predisposition and the most common triggers include allergens such as dust mites, fungal spores, animal epithelia or pollens.
- Rhinoconjunctivitis: Rhinitis is an inflammatory disease of the nasal mucus characterised by nasal congestion and discharge, sneezing and itchy nose. When rhinitis is associated with inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye (conjunctivitis), it is called rhinoconjunctivitis and, in addition to nasal symptoms, patients may experience tearing, itchy eyes, gritty sensation, redness or swelling of the eyes. Like asthma, certain allergens trigger this reaction, such as dust mites, fungal spores, animal dander, pollens or occupational allergens.
It is an exaggerated reaction of the immune system when patients ingest food that they are allergic to. Symptoms appear rapidly (within minutes or 2 hours after ingestion) and are highly variable, ranging from mild (skin reactions) to life-threatening systemic reactions (anaphylaxis). Some of the most frequent are:
- Cutaneous: such as hives and eczema.
- Gastrointestinal: abdominal pain, diarrhoea, nausea and vomiting.
- Respiratory: rhinitis y bronchospasm.
- Cardiovascular: dizziness or a drop in blood pressure. When there is a drop in blood pressure with or without loss of consciousness, an extremely severe allergic reaction known as anaphylactic shock occurs.
It affects 1-3% of the general population and the most common foods that cause allergies are milk, eggs, nuts, wheat, seafood and some fruits. However, any food can cause a food allergy and should be diagnosed by a professional.
Immunological responses to specific drugs. It is estimated that 5% of adults may be allergic to drugs and like food allergies, symptoms are highly variable and can be mild or result in more severe reactions such as anaphylaxis. Common mild reactions include skin reactions such as hives or angioedema. Symptoms may appear immediately or as early as one hour after ingestion.
It is one of the most common skin diseases and usually manifests in childhood. It is characterised by intense itching, skin irritation, eczema lesions and dry skin on certain parts of the body such as the chin, neck, areas near the mouth and the folds of the inner surfaces of the arms and leg. It often occurs in response to food allergic reactions, asthma and rhinitis.
Urticaria is a group of reactions of the superficial part of the skin manifested by skin eruptions, usually in the form of hives or wheals. Outbreaks of urticaria are often associated with allergic reactions caused by food or medication, however due to the rapid nature of food and drug allergies, these allergies are usually ruled out as triggers. In most cases of urticaria, the cause of the rash cannot be ascertained, except in children, where outbreaks are associated with infections.
Angioedema, unlike urticaria, causes lesions that affect the deeper layers of the skin, forming deep swellings that often appear on the face. Occasionally, these swellings can be experienced on the tongue, leading to difficulty in breathing and often require medical attention. There are several types but the most common is histaminergic, which arises in response to an allergic reaction to drugs, especially the aspirin group.
Humans are exposed to an infinite number of organisms that can cause aggressions through stings or bites. Among them, the Hymenoptera species include bees, bumblebees, wasps and hornets. These insects release different types of venom which very often act as allergens that trigger skin reactions in the area of inoculation and severe systemic reactions (anaphylaxis).
We look after you allergies.
Don't let allergies control your everyday life! Our specialists will help you diagnose, treat and prevent your allergies.

What does an allergology consultation at Turó Park Clinics consist of ?
To make a diagnosis, the specialist will evaluate your medical history, symptoms and possible triggers. Diagnostic tests may then be performed to determine the main cause of the allergy:
Common to assess respiratory allergies such as asthma or rhinoconjunctivitis. They consist of a set of tests that assess lung function and its ability to take in and release air, as well as to exchange gases efficiently. They also help to identify the condition of the airways and may include spirometry, lung volume, airway resistance and pulse oximeter tests.
It assesses the immune system's response to different allergens introduced to the surface of the skin by means of a gentle prick.
They are common for cases where the prick test is negative and for more sensitive cases where the suspected allergen is the hymenoptera venom or drugs. Unlike the prick test, the allergen extract is inoculated into a deeper layer of the skin.
They are crucial for identifying the presence of an allergic reaction, assessing antibody production and identifying the allergen causing the reaction. They usually complement skin tests.
Crucial to confirm the presence, determine the severity and develop a management plan for an allergy that stems from the use of certain medications. These tests may include a prick test, patch tests or blood tests.
As a complement to the different tests, it is common to perform other diagnostic tests such as stool tests or controlled exposure tests with food and drugs. Controlled exposure tests consists of the progressive administration of the drug or food responsible for the reaction and monitoring the patient's reaction over a period of 1 to 4 hours.
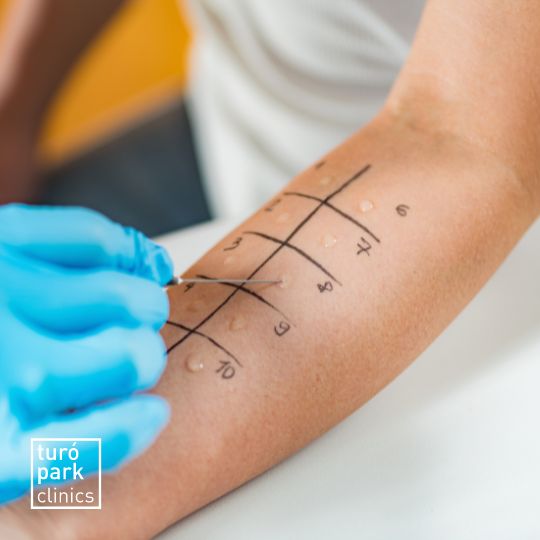
What is a prick test and how is it performed?
A prick test is an immediate reaction test performed to help us identify whether a person is allergic to a specific substance. Given the speed and high sensitivity of this test, it is a very safe and recommendable option for diagnosing possible allergies to pollens, insects, drugs and mites, among many others.
This test is performed by applying small drops of allergen extract to the skin (usually on the forearm or back) and gently pricking the skin with a lancet. The doctor will then wait 15-20 minutes to observe the skin reaction and look for signs of an allergic reaction. It is considered positive if a wheal or welt with a diameter of at least 3 mm appears after the waiting time.
Treatment: specific immunotherapy
Specific immunotherapy or allergy vaccine, is a treatment that involves the administration of an allergen in a controlled manner over a period of 3 to 5 years. It is administered by injection or by sublingual drops or tablets and its aim is to 'train' the immune system to stop recognising the allergen as a threat and therefore ceasing to produce an allergic reaction while developing a tolerance to the allergen.
The vaccine can reduce or even make the need for symptomatic medication to go away and is a very effective and safe option for people suffering from persistent allergies to wasp stings, pollen, mites, drugs and animal epithelia. In the case of allergy to hymenoptera venom, specifically wasp venom, vaccines have been shown to cure more than 95% of patients allergic to it.
The vaccine is an accessible and beneficial option for any allergic patient regardless of age. However, it is recommended to vaccinate children once they have reached 5 years of age, as it is common for them to have respiratory infections that can easily be mistaken for allergic reactions.
Our allergy prevention tips
To manage and prevent allergies, consider the following tips:
- Avoid Allergens: Identify and try to avoid your allergy triggers.
- Regular Cleaning: Keep your home clean to reduce exposure to dust mites and mould
- Use of Medication: Follow your allergist's advice on the use of antihistamines, inhalers or other medications.
- Immunotherapy: If you have opted for this treatment, follow your allergist's guidelines for allergy shots. Such treatment can reduce sensitivity to allergens over time.
- Environmental control: Use air filters, dehumidifiers and other devices to improve the air quality in your home.
- Education: Get information about your allergies and learn how to manage them effectively.
Fast track your booking
To make an appointment or speak to a member of our team, please get in touch using the following options